- Home
- How Likely is a U.S. Bullet Train to Match Japan’s Shinkansen Speed?
How Likely is a U.S. Bullet Train to Match Japan’s Shinkansen Speed?
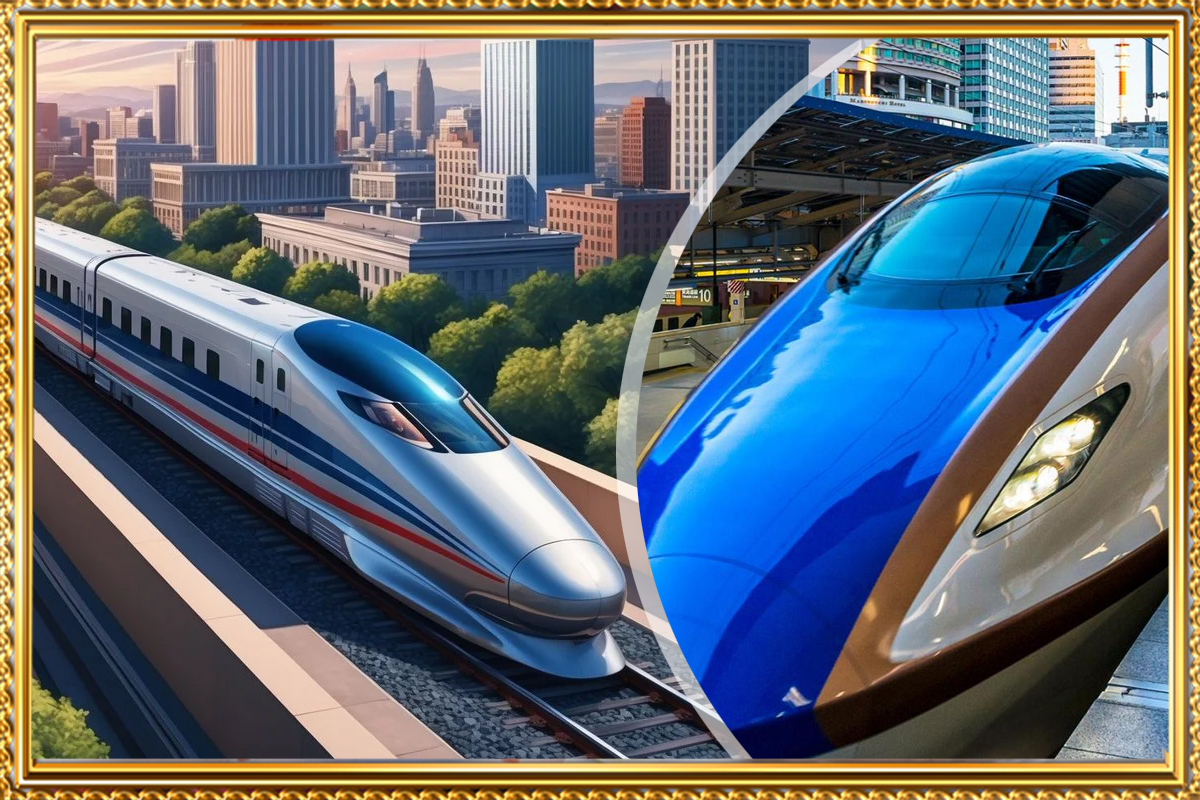

Japan’s Shinkansen, often referred to as the "bullet train," is a marvel of modern engineering, renowned for its speed, safety, and efficiency. With a maximum operating speed of up to 320 km/h (199 mph), it has set benchmarks for high-speed rail systems worldwide. The United States, a global leader in innovation, has long debated introducing its own high-speed rail system. But can America build a bullet train as fast or faster than the Shinkansen? Which routes would be most suitable for such a project?
This article explores the feasibility of high-speed rail in the U.S., compares the Shinkansen to existing systems, and examines the benefits and drawbacks of introducing such technology stateside.
The Maximum Speed of Japan’s Shinkansen
How Japan’s Shinkansen System Works
Suitability of High-Speed Rail Routes in the U.S.
Advantages of the Shinkansen
Drawbacks of the Shinkansen
Why the U.S. Should Invest in High-Speed Rail
Technological Innovations for U.S. High-Speed Rail
Additional Points for Consideration
Positive Aspects of Shinkansen for the U.S.
Negative Aspects
FAQs
CONCLUSION
The Maximum Speed of Japan’s Shinkansen
The fastest Shinkansen model, the E5 Series, reaches a top operating speed of 320 km/h (199 mph). Future advancements, like the maglev-based Chūō Shinkansen, are projected to exceed 500 km/h (311 mph). These high speeds are achieved through several cutting-edge technologies:
- Aerodynamic Design: Streamlined train shapes minimize air resistance.
- Advanced Track Systems: Dedicated high-speed rail tracks eliminate delays and optimize performance.
- Precision Engineering: Superior construction materials and vibration-damping systems enhance stability.
- State-of-the-Art Signaling: Automated controls ensure optimal speed and safety.
- However, high-speed trains face drawbacks like high construction costs, noise pollution, and the need for regular maintenance to uphold safety and speed standards.

How Japan’s Shinkansen System Works
The Shinkansen operates on dedicated tracks built for high-speed travel, separated from traditional rail systems. Key factors contributing to its efficiency and safety include:
- Dedicated Infrastructure: Tracks are built on elevated viaducts or in tunnels to avoid intersections with roads.
- Automatic Train Control (ATC): Advanced systems monitor and adjust speed in real-time to prevent accidents.
- Earthquake Detection: Sensors halt trains during seismic activity, ensuring passenger safety.
- Rigorous Maintenance: Frequent inspections keep trains and tracks in top condition.
Suitability of High-Speed Rail Routes in the U.S.
The U.S. has vast land areas and urban clusters ideal for high-speed rail. Promising routes include:
- California Corridor: Linking Los Angeles to San Francisco could significantly reduce traffic and flight congestion.
- Northeast Corridor: A Boston-to-Washington D.C. line could modernize the busiest rail route in the U.S.
- Texas Triangle: Connecting Dallas, Houston, and Austin would cater to a growing population and economy.
Advantages of the Shinkansen
- Safety: Zero passenger fatalities since its launch in 1964.
- Punctuality: Average delays measured in seconds.
- Environmental Benefits: Low carbon emissions compared to cars and planes.
- Economic Growth: Boosts tourism and regional development.
Drawbacks of the Shinkansen
- High Costs: Construction and maintenance require substantial investment.
- Noise Pollution: High speeds generate significant noise in residential areas.
- Limited Flexibility: Dedicated tracks restrict integration with traditional rail.
Why the U.S. Should Invest in High-Speed Rail
- Economic Benefits: High-speed rail could create jobs, stimulate local economies, and enhance productivity by reducing travel time.
- Environmental Impact: A rail system powered by renewable energy would cut greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improved Mobility: Linking major cities with high-speed trains would revolutionize intercity travel.
Technological Innovations for U.S. High-Speed Rail
- Maglev Technology: The U.S. could explore maglev (magnetic levitation) trains, which can reach speeds exceeding 500 km/h (311 mph). Implementing this technology would position the U.S. as a leader in transportation innovation.
- Hybrid Energy Systems: Integrating renewable energy sources like solar or wind into the rail system's power grid could enhance sustainability.
- AI Integration: Advanced artificial intelligence could optimize scheduling, maintenance, and energy efficiency, reducing operational costs.
Additional Points for Consideration
- Environmental Impact: 1. Reduction in Air Travel: High-speed rail could significantly reduce the number of short-haul flights, cutting aviation-related carbon emissions. 2. Urban Sustainability: Encouraging high-speed rail use could decrease car dependency, reduce urban sprawl, and promote sustainable urban planning.
- Sociocultural Impact: 1. Changing Perceptions: Educating the public about the benefits of high-speed rail could help overcome resistance in car-dependent regions. 2. Accessibility Enhancements: Designing stations with accessibility features could ensure the rail system benefits all demographics, including elderly and disabled passengers.
- Shinkansen vs. Regular Trains: A Shinkansen train can reach speeds nearly three times faster than conventional trains. While regular trains average 80-100 km/h (50-62 mph), Shinkansen’s advanced technology delivers unparalleled speed and reliability.
- Shinkansen vs. Bullet Train: What’s the Difference? The term "bullet train" is often used interchangeably with "Shinkansen." However, "Shinkansen" specifically refers to Japan’s high-speed rail network, while "bullet train" is a broader term encompassing similar systems globally.
- Why Japanese Shinkansen Are Faster Than European High-Speed Trains: Japan’s Shinkansen benefits from dedicated infrastructure, whereas European systems often share tracks with conventional trains, limiting speeds. Additionally, Japan’s investment in advanced safety and automation technologies surpasses most other systems.
Positive Aspects of Shinkansen for the U.S.
- Faster Travel: High-speed rail would offer a competitive alternative to short-haul flights.
- Urban Connectivity: Improved access between cities could promote balanced regional development.
- Innovation Hub: The U.S. could lead advancements in high-speed rail technology.
Negative Aspects
- Infrastructure Challenges: Land acquisition and construction could face delays.
- Initial Costs: High-speed rail systems demand significant upfront investment.
- Public Acceptance: Changing car-dependent culture might be slow.
FAQs
- What’s the fastest bullet train in Japan? The E5 Series Shinkansen operates at speeds up to 320 km/h (199 mph).
- Is the Shinkansen affordable? While prices are higher than conventional trains, rail passes and discounts improve accessibility.
- Could the U.S. build a faster train than the Shinkansen? Technologically, yes. However, economic and infrastructure hurdles must be addressed.
- Why is the Shinkansen considered safe? Features like automatic control systems and earthquake detection ensure passenger safety.
- Which U.S. route is most suitable for a bullet train? The California Corridor (Los Angeles to San Francisco) and the Northeast Corridor (Boston to Washington D.C.) are top candidates.
Economic Considerations: 1. Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations between government and private entities could alleviate the financial burden of building high-speed rail. 2. Tourism Boost: High-speed rail could encourage domestic tourism by making travel between cities faster and more convenient. 3. Long-Term ROI: Although initial investments are high, studies show that high-speed rail can yield substantial economic returns over decades through job creation and regional development.
Affordability and Accessibility of the Shinkansen: While ticket prices can be high, rail passes and discount options make the Shinkansen accessible to travelers. However, costs may deter daily commuters.

Conclusion: The U.S. has the potential to develop a high-speed rail system rivaling Japan’s Shinkansen. By focusing on suitable routes, advanced technology, and sustainable practices, America could transform its transportation landscape. While challenges exist, the benefits of high-speed rail—economic growth, environmental sustainability, and improved connectivity—make it a worthy investment for the future.
0 Comments
Top Rated Adventure
Where to Find the Best Holiday Decorations and Free Tours in Washington D.C.
- 25 Nov 2024
- 0 0

















Post a comment