- Home
- How to Protect Your Home from California Wildfires
How to Protect Your Home from California Wildfires
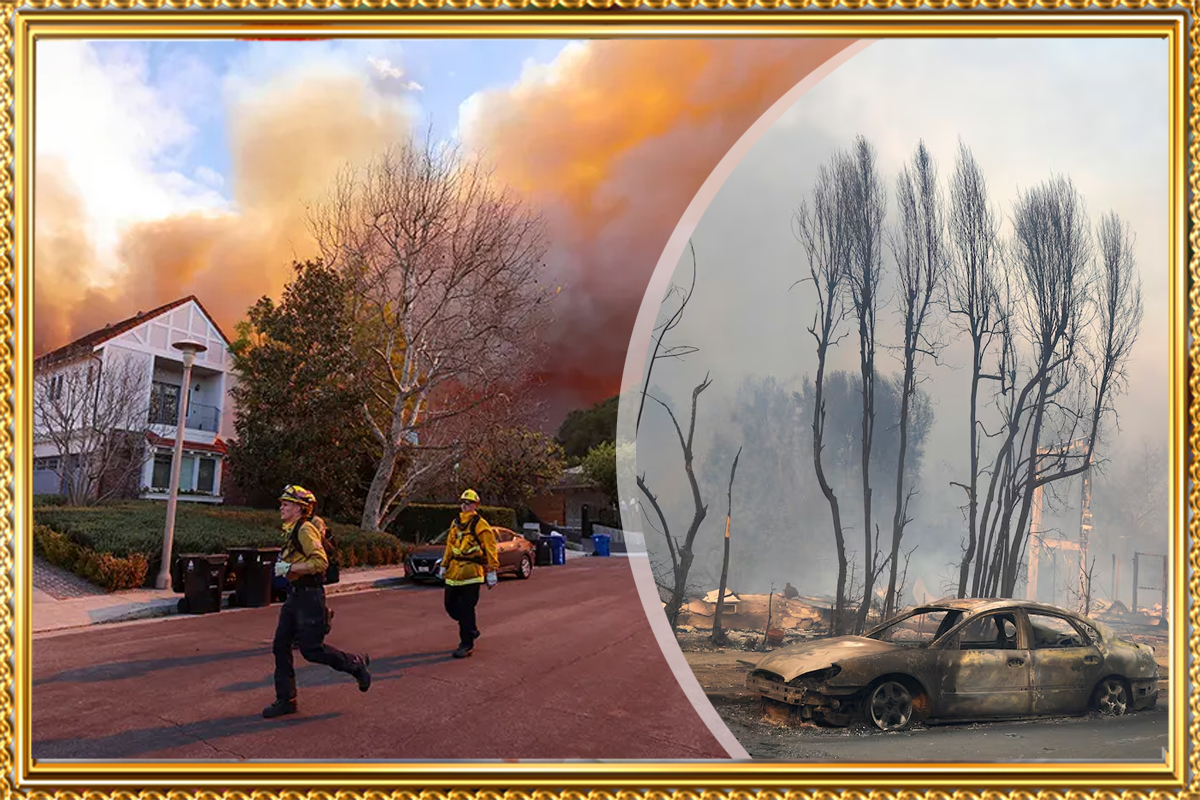

Learn why California experiences frequent wildfires, their causes, and the challenges in controlling them. Discover preventative measures and strategies to reduce wildfire damage and protect communities.
California has long been synonymous with natural beauty, from its iconic beaches to its sprawling forests. However, the state is equally notorious for its wildfires, which have increased in frequency and intensity over the years. This blog explores the reasons behind California’s wildfire problem, the challenges in combating these fires, and strategies to prevent and reduce their devastating impact.
Why is California Prone to Wildfires?
Causes of Wildfires in California
Challenges in Fighting Wildfires
Preventative Actions to Reduce Wildfires
Innovative Technologies in Fighting Wildfires
Impact of Wildfires on Water Resources
Role of Indigenous Practices
Positive Aspects of Wildfires
Negative Aspects of Wildfires
FAQs
CONCLUSION
Why is California Prone to Wildfires?
California’s unique geography, climate, and vegetation make it particularly susceptible to wildfires. Here are the key factors:
- Dry Climate: California’s Mediterranean climate is characterized by long, dry summers and minimal rainfall, creating the perfect conditions for wildfires.
- Vegetation: The state is home to vast forests, grasslands, and shrubs that act as natural fuel for fires. Prolonged droughts further dry out this vegetation, making it highly flammable.
- Santa Ana Winds: These hot, dry winds exacerbate fires by spreading flames rapidly and fueling their intensity.
- Urban-Wildland Interface: As urban areas expand into wildlands, human activities like construction and recreation increase the risk of igniting fires.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and prolonged droughts due to climate change are worsening the wildfire season, extending its duration and increasing fire intensity.

Causes of Wildfires in California
While natural factors play a role, human activities are the leading cause of wildfires:
- Electrical Equipment Failures: Power lines and electrical equipment malfunctions have been responsible for some of the most devastating wildfires, such as the Camp Fire in Paradise.
- Human Negligence: Campfires left unattended, discarded cigarettes, and illegal fireworks often ignite wildfires.
- Arson: Intentional acts of arson account for a significant number of fires annually.
- Lightning Strikes: While less common, lightning strikes during thunderstorms can ignite fires, especially in dry regions.
Challenges in Fighting Wildfires
- Rapid Spread: Factors like wind and dry vegetation cause fires to spread quickly, often outpacing firefighting efforts.
- Difficult Terrain: Many fires occur in remote, mountainous areas that are hard to access.
- Resource Limitations: Firefighting requires substantial manpower, equipment, and funding, which can strain resources during peak wildfire season.
- Air Quality Concerns: Wildfires produce thick smoke, posing health risks to firefighters and residents alike.
- Prolonged Fire Season: The fire season has expanded, making it harder for teams to manage consecutive incidents.
Preventative Actions to Reduce Wildfires
California has implemented several strategies to prevent wildfires and minimize their damage. These include:
- Controlled Burns: Prescribed burns remove excess vegetation, reducing the amount of fuel available for wildfires.
- Vegetation Management: Clearing brush and dead trees in high-risk areas helps mitigate fire hazards.
- Upgrading Power Infrastructure: Utilities are investing in fire-resistant equipment and implementing public safety power shutoffs during high-risk periods.
- Community Education: Raising awareness about fire safety, such as safe camping practices and emergency preparedness, can reduce human-caused fires.
- Improved Building Codes: Homes in fire-prone areas are being constructed with fire-resistant materials to withstand wildfires.
Innovative Technologies in Fighting Wildfires
- AI and Satellite Monitoring: Advanced systems use satellite imagery and artificial intelligence to detect fires early and predict their spread, allowing for quicker response times.
- Drones: Unmanned aerial vehicles are increasingly being used to survey fire-affected areas, assess damage, and drop fire retardants in hard-to-reach locations.
- Fire-Resistant Fabrics: Development of fireproof materials for uniforms, shelters, and homes in fire-prone areas enhances safety and resilience.
Impact of Wildfires on Water Resources
- Water Quality Degradation: Wildfires can contaminate water sources with ash, sediment, and fire retardants, leading to long-term water quality issues.
- Watershed Damage: Fires disrupt watershed ecosystems, reducing their capacity to manage storm water and increasing the risk of flooding post-fire.
Role of Indigenous Practices
- Traditional Fire Management: Indigenous communities have historically used controlled burns to manage forests and grasslands, promoting healthy ecosystems and reducing large-scale fire risks.
- Cultural Significance: Recognizing and integrating indigenous knowledge into modern wildfire management strategies can provide sustainable and effective solutions.
Positive Aspects of Wildfires
Although devastating, wildfires play a natural role in maintaining forest health:
- Ecosystem Renewal: Fires clear dead vegetation, allowing new growth and increasing biodiversity.
- Nutrient Recycling: Burning releases nutrients into the soil, enriching it for future plant growth.
- Pest Control: Fires help control invasive species and pests, preserving the balance of native ecosystems.
Negative Aspects of Wildfires
The negative impacts of wildfires often overshadow their ecological benefits:
- Loss of Life and Property: Wildfires destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure, displacing thousands of residents.
- Environmental Damage: Fires contribute to deforestation, soil erosion, and loss of wildlife habitats.
- Economic Impact: The cost of fighting fires and rebuilding communities is enormous, burdening state and local budgets.
- Health Issues: Smoke and air pollution cause respiratory problems, particularly for vulnerable populations.
FAQs
- Is every area in California prone to wildfires? While wildfires can occur throughout California, regions with dense forests, dry grasslands, and chaparral are at higher risk.
- Why did Paradise, California burn to the ground? The Camp Fire, fueled by dry conditions and sparked by electrical equipment, devastated Paradise in 2018. Poor evacuation planning and high winds exacerbated the disaster.
- Can wildfires in California be completely prevented? While it’s impossible to eliminate wildfires entirely, proactive measures like controlled burns, improved infrastructure, and public education can significantly reduce their frequency and impact.
- Are there parts of California safe from wildfires? Coastal areas and urban centers with less vegetation are generally less prone to wildfires, but no region is entirely immune.
- Why does California experience wildfires year after year? A combination of dry climate, abundant vegetation, human activity, and climate change contributes to California’s recurring wildfire problem.
Conclusion

While wildfires are a natural part of the state’s ecosystem, their increasing frequency and intensity pose significant challenges. Through a combination of preventative measures, improved firefighting techniques, and community education, California can better manage and mitigate the impact of wildfires. Protecting lives, property, and the environment requires a collective effort and continued innovation.
0 Comments
Top Rated Adventure
Where to Find the Best Holiday Decorations and Free Tours in Washington D.C.
- 25 Nov 2024
- 0 0

















Post a comment